Study AMSI
AMSI (Anti-Malware Scan Interface) is a PowerShell security feature that will allow any applications or services to integrate directly into anti-malware products. Defender instruments AMSI to scan payloads and scripts before execution inside the .NET runtime.
From Microsoft: “The Windows Antimalware Scan Interface (AMSI) is a versatile interface standard that allows your applications and services to integrate with any anti-malware product that’s present on a machine. AMSI provides enhanced malware protection for your end-users and their data, applications, and workloads.”
AMSI will determine its actions from a response code as a result of monitoring and scanning:
AMSI_RESULT_CLEAN = 0
AMSI_RESULT_NOT_DETECTED = 1
AMSI_RESULT_BLOCKED_BY_ADMIN_START = 16384
AMSI_RESULT_BLOCKED_BY_ADMIN_END = 20479
AMSI_RESULT_DETECTED = 32768
These response codes will only be reported on the backend of AMSI or through third-party implementation. If AMSI detects a malicious result, it will halt execution and send an error message.
PS C:Users\Tryhackme> 'Invoke-Hacks'
At line:1 char:1
+ "Invoke-Hacks"
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
This script contains malicious content and has been blocked by your antivirus software.
+ CategoryInfo : ParserError: (:) []. ParentContainsErrorRecordException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : ScriptContainedMaliciousContent
AMSI is fully integrated into the following Windows components:
User Account Control, or UAC
PowerShell
Windows Script Host (wscript and cscript)
JavaScript and VBScript
Office VBA macros
When targeting the above components, attackers need to be mindful of AMSI and its implementations when executing code or abusing components.
The way AMSI is instrumented can be complex, including multiple DLLs and varying execution strategies depending on where it is instrumented. By definition, AMSI is only an interface for other anti-malware products; AMSI will use multiple provider DLLs and API calls depending on what is being executed and at what layer it is being executed.
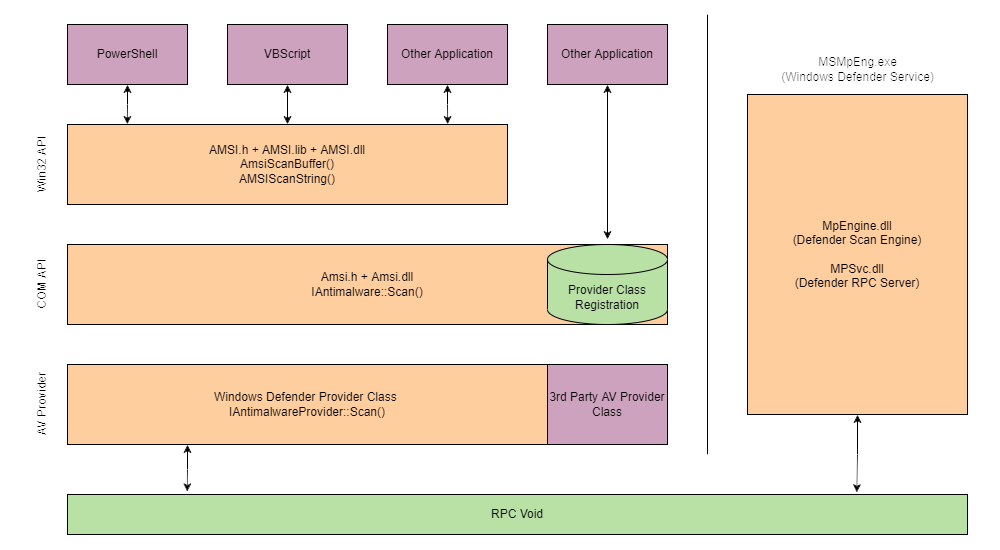 |
|---|
| How data is dissected as it flows through the layers and what DLLs/API calls are being instrumented. |
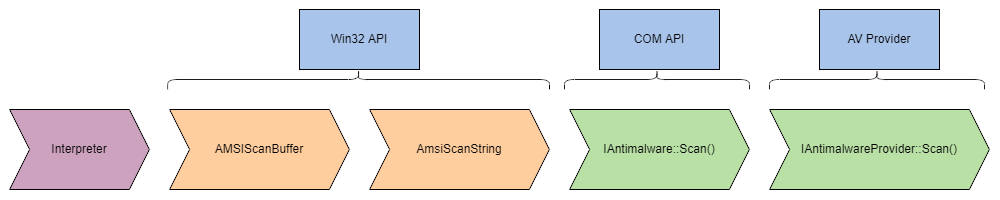 |
|---|
| Break down into core components. |
Note: AMSI is only instrumented when loaded from memory when executed from the CLR. It is assumed that if on disk
MsMpEng.exe (Windows Defender) is already being instrumented.
Most of the known bypasses are placed in the Win32 API layer, manipulating the AmsiScanBuffer API call.
To find where AMSI is instrumented, use InsecurePowerShell, a GitHub fork of PowerShell with security features removed.
Look through the compared commits and observe any security features. AMSI is only instrumented in twelve lines of
code under src/System.Management.Automation/engine/runtime/CompiledScriptBlock.cs:
var scriptExtent = scriptBlockAst.Extent;
if (AmsiUtils.ScanContent(scriptExtent.Text, scriptExtent.File) == AmsiUtils.AmsiNativeMethods.AMSI_RESULT.AMSI_RESULT_DETECTED)
{
var parseError = new ParseError(scriptExtent, "ScriptContainedMaliciousContent", ParserStrings.ScriptContainedMaliciousContent);
throw new ParseException(new[] { parseError });
}
if (ScriptBlock.CheckSuspiciousContent(scriptBlockAst) != null)
{
HasSuspiciousContent = true;
}